

Ceurf Course Online
Using a double training in medical intensive care and ultrasound, Prof. Daniel Lichtenstein has developed since 1989 the use of general ultrasound applied to the intensive care, in the University Hospital Ambroise Paré (AP-HP), in François Jardin’s medical ICU.
Prices
Basic
2,99€Every monthThe basics of Lung UltrasoundIntermediate
5,99€Every monthThe BLUE ProtocolAdvanced
8,99€Every monthHolistic Whole Body UltrasoundStandard
200€Valid for one year- Unlimited access to videos - 1 Year
- Watch on any device
- CEURF Certification of completion
Premium
465€Valid for one year- Unlimited access to videos - 1 Year
- Watch on any device
- CEURF Certification of completion
- Discount of 100% on presential CEURF Course around the world
- eBook "Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill"
- Q & A Prof. D. Lichtenstein
- Access to new content
PROGRAMME
Ultrasound devoted to the critically ill - Introduction
Tool
Heart
LUCI
DVT
The BLUE-Protocol
The FALLS-Protocol
Venous Line
The LUCI-FLR Program
Head
Abdomen
Trauma
The SESAME-Protocol

Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill (LUCI)
and Critical Ultrasound: How Did All This
Happen? A (Not So) Short Introduction
“Some precious colleagues from various centers, including Raul Laguarda in Boston, Beth Powell and Jeff Handler in Toronto, Mike Welsh in Indianapolis, and German Moreno-Aguilar in Colombia, have efficiently transmitted the holistic spirit of lung ultrasound in the manner of CEURF”
The Unit: A perfect harmony
The ADR-4000® and the Hitachi 405. Our references:
two respectable collector machines, yet perfectly
mobile to the bedside and able to achieve the ultrasound
revolution since 1982 ( left ) and 1992 ( right ). Both are
small in width ( left , 42 cm, right , 32 cm), and both have
wheels, the key to the revolution.

Revolution is not resolution...

A backward step of 25 years. A nice revolution (the laptops), but a questionable resolution. This figure summarizes a small drama in the history of (lung) ultrasound. From top to bottom (top, our ADR-4000) (middle, our Hitachi 405); note in the bottom line how the image quality has worsened. The bottom line (modern laptop) shows the way many physicians discovered lung ultrasound. Please just compare: a backward jump of 25 years for no gain of space.

The Probe: Simply universal
Our universal microconvex probe. This probe is
80 g light, 88-mm long and has a 12 x 20 mm footprint.
The frequency is 5 MHz, but this probe just shows, from 6
to 170 mm of penetration, what is in the explored field,
regardless if the surface is linear or not. A simple probe,
which changes the landscape of critical ultrasound
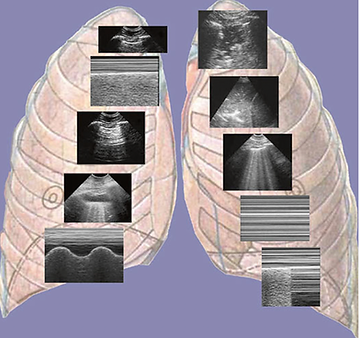
Ten basics signs :)
The ten basic signs for the lung part of the BLUE-protocol. The first sign, from the left and the top, is the basis (the bat sign). The second and third are signs of normality (A-lines and lung sliding). The rest are pleural effusion (quad sign, sinusoid sign), lung consolidation (shred sign, tissuelike sign), interstitial syndrome (lung rockets), and pneumothorax (stratosphere sign and lung point – the A-line sign is already featuring). The only color is the one of the background, for esthetic purpose. No space for Doppler in LUCI. Nice figure indeed (which
inspired some manufacturers)
The BLUE Protocol

The BLUE-Protocol (for patients in acute respiratory failure) is based on the seven principles of lung ultrasound, mastery application of ten signs for building eight profiles and make the diagnoses of six principals diseases (97% of the patients): pulmonary embolism, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma and pneumothorax, with accuracy of 90.5% in comparison with the gold standard: Computed Tomography.

The FALLS Protocol
The FALLS-Protocol (for patients in acute circulatory failure) permit the sequential diagnosis of the Shock: obstructive, cardiogenic, hypovolemic and distributive and use of an on-off marker of volemia (lung rockets) while the fluid therapy is done continuously in patients called “FALLS-responders”.
The SESAME Protocol
The SESAME-Protocol accompanying of the ECG permit the diagnosis of the principal causes than conduce the patient to cardiac arrest
